PortSwigger Lab: 2FA Simple Bypass
Introduction:
Two-factor authentication (2FA) serves as a critical security layer for protecting user accounts, but improper implementation can render this protection ineffective. This lab demonstrates a common vulnerability where applications fail to properly enforce 2FA verification, allowing attackers to bypass the authentication process entirely by manipulating navigation flow.
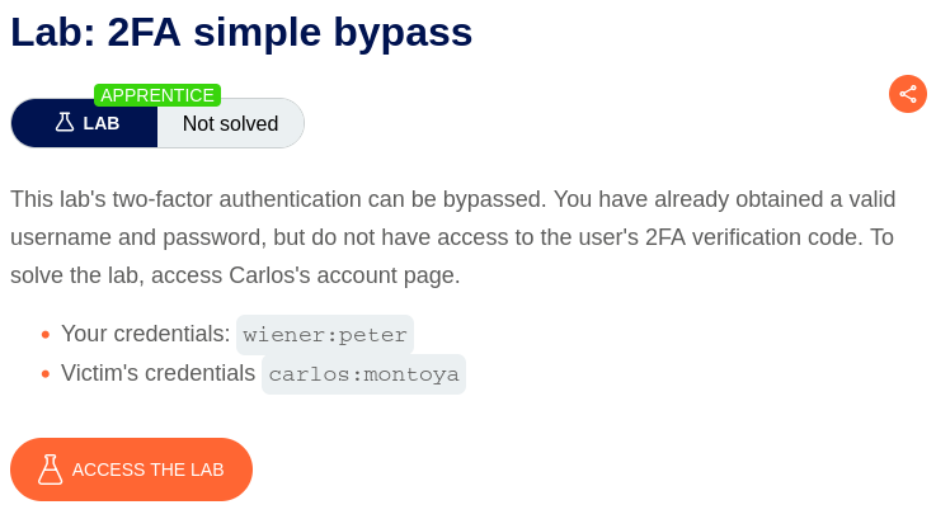
Lab Setup and Objective:
The lab simulates a web application with 2FA functionality that sends verification codes via email. The objective is to demonstrate how inadequate session state management after initial authentication can allow attackers to skip the 2FA verification step and directly access protected resources.
Detailed Walkthrough
Normal Authentication Flow Analysis:
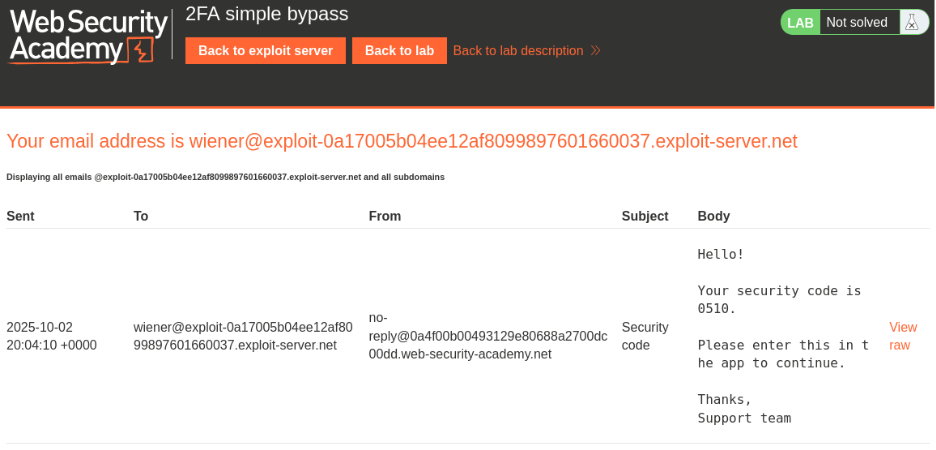
The process begins with logging into a legitimate account to understand the normal authentication workflow. After entering credentials, the application redirects to a 2FA verification page where a code is sent via email. Accessing the email client confirms receipt of the verification code, and completing this step grants access to the account page at `/my-account`.
Identifying the Vulnerability:
After logging out and authenticating with victim credentials, the application correctly prompts for the 2FA verification code. However, instead of submitting the code, the URL is manually modified to directly navigate to `/my-account`. Surprisingly, this bypasses the 2FA requirement entirely, granting full access to the victim’s account and solving the lab.
Technical Insights
Vulnerability Analysis:
This bypass occurs due to insufficient session state validation on protected pages. The application successfully authenticates the user’s credentials but fails to verify that the 2FA step has been completed before granting access to sensitive areas. The `/my-account` endpoint lacks proper checks to ensure users have completed the full authentication process.
Attack Vector Characteristics:
The primary attack vector exploits:
- Inadequate session state management
- Missing access control checks on protected endpoints
- Failure to enforce multi-step authentication workflows
- Predictable URL structures for sensitive resources
Mitigation Strategies:
- Proper Session State Management: Applications must track the complete authentication state, ensuring users cannot access protected resources until all authentication steps are completed. Session objects should include flags indicating whether each authentication factor has been verified.
- Comprehensive Access Control: Every protected endpoint should validate that users have completed the full authentication process, including all required factors. This validation should occur server-side and cannot rely solely on client-side controls.
- Forced Navigation: After successful credential authentication but before 2FA completion, users should be restricted to only the 2FA verification pages. Any attempt to access other parts of the application should redirect back to the verification flow.
- Stateful Authentication Tokens: Implement tokens that track authentication progress, ensuring tokens issued after the first factor are different from those issued after completing all factors.
- Security Headers and Controls: Implement proper security headers and session configurations that prevent unauthorized access to protected resources during incomplete authentication states.
Conclusion:
This lab highlights a critical flaw in 2FA implementation where the additional security factor can be completely circumvented through simple navigation manipulation. The vulnerability stems from treating credential authentication and second-factor verification as separate, independent processes rather than components of a unified authentication workflow. Organizations implementing multi-factor authentication must ensure comprehensive session management and access controls that enforce completion of all authentication steps before granting access to protected resources.
References:
– PortSwigger Web Security Academy: [https://portswigger.net/web-security](https://portswigger.net/web-security)
– OWASP Authentication Cheat Sheet: [https://cheatsheetseries.owasp.org/cheatsheets/Authentication_Cheat_Sheet.html](https://cheatsheetseries.owasp.org/cheatsheets/Authentication_Cheat_Sheet.html)
– NIST Digital Identity Guidelines: [https://pages.nist.gov/800-63-3/](https://pages.nist.gov/800-63-3/)