Vulnerability Type: Reflected Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)

Attack Vector
The vulnerable application reflects user input directly into the HTML response without encoding or sanitization, allowing arbitrary JavaScript execution. The attack vector leverages a simple search functionality where the input is embedded unfiltered into the page’s HTML.
Exploitation Steps
- Identify the Input Vector: A search form reflects user input directly in the HTML response.
- Craft Malicious Payload: Inject a JavaScript payload via the search parameter; <script>alert(1)</script>
- Trigger the Exploit:
- Paste the payload into the search box and submit.
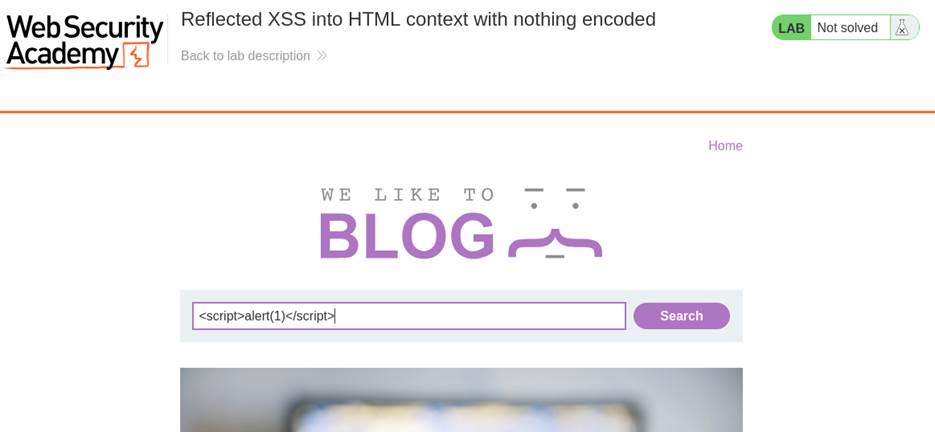
- The server reflects the input un-sanitized, causing the browser to execute the `alert(1)` script.
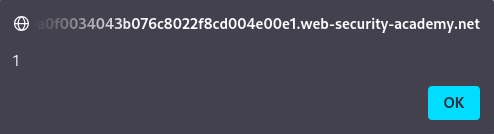
- Confirmation: A pop-up with “1” confirms successful XSS exploitation.
Mitigation Strategies
- Output Encoding: Encode user input before embedding it in HTML (e.g., HTML entity encoding).
– Example: Convert `<script>` to `<script>`.
- Input Validation: Restrict input to expected patterns (e.g., alphanumeric for search queries).
- Content Security Policy (CSP): Implement CSP headers to restrict inline scripts.
- Framework Protections: Use modern frameworks (e.g., React, Angular) that auto-escape dynamic content.
Key Takeaway
This lab demonstrates the danger of trusting user-supplied input without validation or encoding. Even a basic script tag can compromise session integrity, highlighting the need for defense-in-depth measures.





