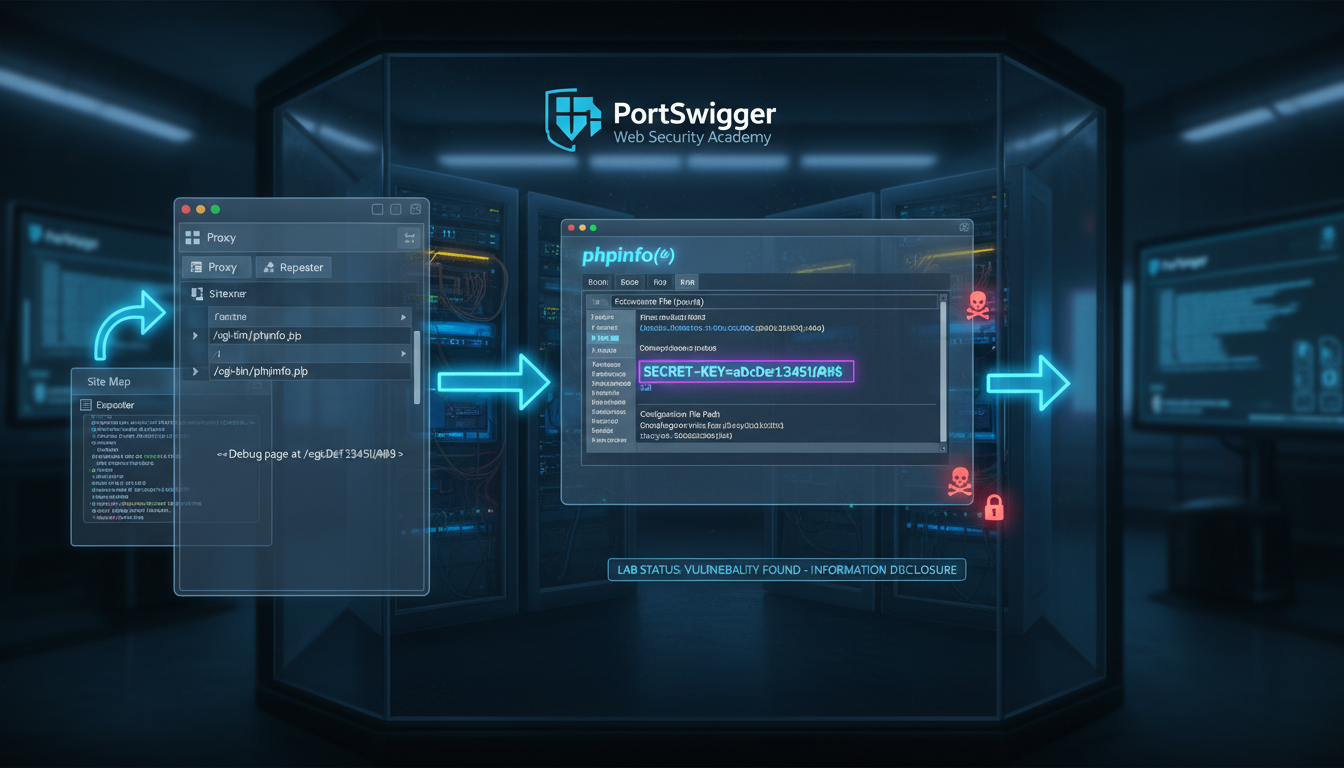
This lab demonstrates a common vulnerability where sensitive information is exposed through a debug page. Applications often include diagnostic or debugging interfaces intended for development or administrative purposes. When these pages are accessible in production environments without proper access controls, they can leak critical information, such as environment variables, configuration details, or credentials.
Attack Vector Used:
The primary attack vector involves discovering hidden or unintended endpoints that expose debugging information. In this case, an HTML comment embedded in the homepage source code references a debug page (`/cgi-bin/phpinfo.php`). This page, when accessed, reveals extensive configuration details, including sensitive environment variables.
Exploitation Steps:
- Discover Hidden Links: While proxying traffic through Burp Suite, navigate to the homepage and inspect the source for any hidden links or comments. The Target > Site Map feature can assist in identifying unusual paths.
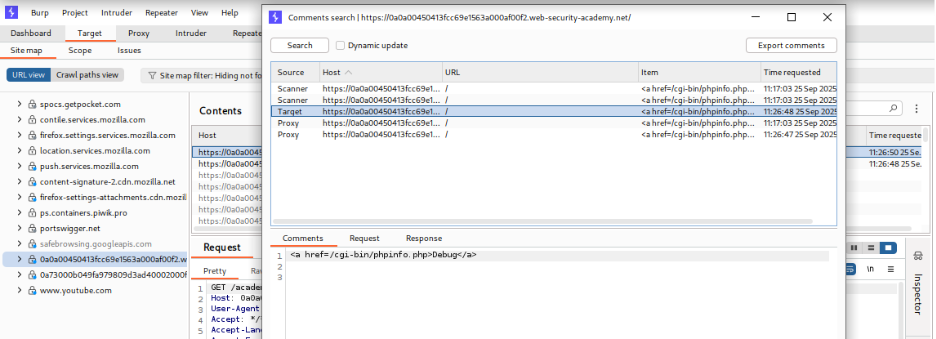
- Locate Debug Page: Identify the `/cgi-bin/phpinfo.php` endpoint referenced in an HTML comment.
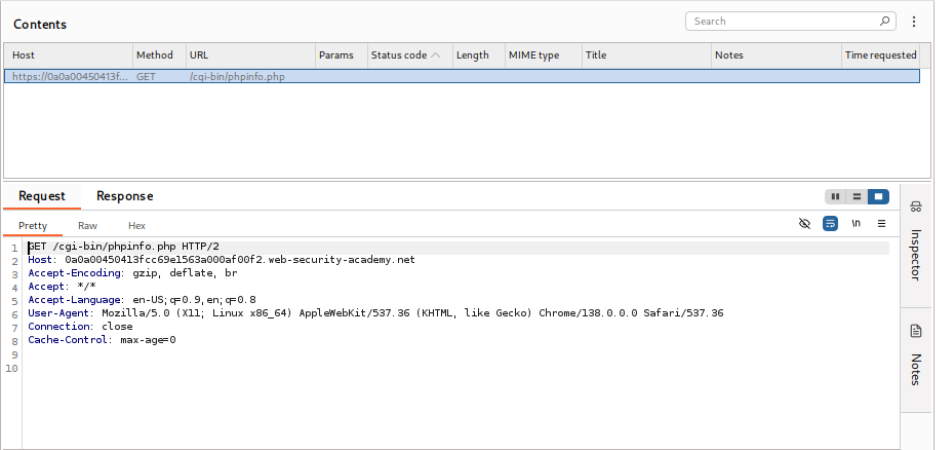
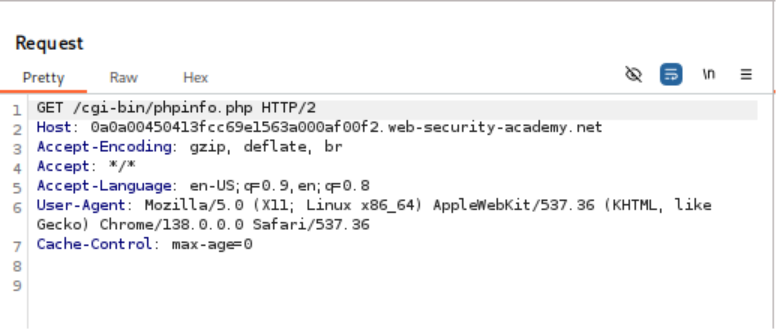
- Access Debug Page: Send a request to the debug page using Burp Repeater.
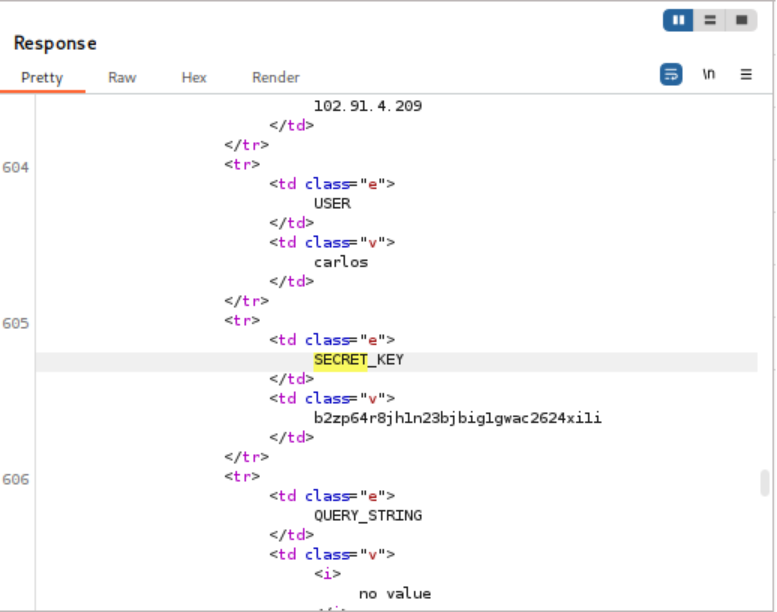
- Extract Sensitive Data: Review the response to locate sensitive information. In this instance, the `SECRET_KEY` environment variable is exposed.
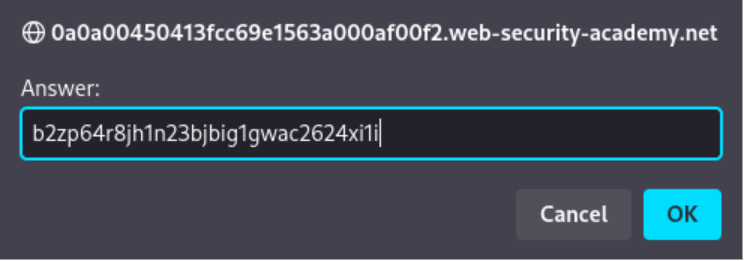
- Complete the Lab: Submit the discovered `SECRET_KEY` to solve the lab.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Remove Debug Interfaces: Ensure that debugging pages or interfaces are removed or disabled in production environments. These should only be accessible during development or to authorized personnel.
- Restrict Access: Implement strong access controls, such as authentication and IP whitelisting, for any administrative or diagnostic interfaces that must remain accessible.
- Scan for Exposed Files: Regularly scan the application for unintended files or endpoints that may expose sensitive information. Tools like Burp Suite’s “Site Map” or automated crawlers can assist with this.
- Review Source Code: Avoid embedding sensitive comments or metadata in HTML or client-side code. Conduct regular reviews to ensure no accidental exposure occurs.
- Environment Variable Management: Avoid storing sensitive keys or credentials in environment variables that might be exposed through debug interfaces. Use secure credential management systems instead.
By applying these mitigation techniques, organizations can reduce the likelihood of exposing sensitive information through debug pages, minimizing potential attack surfaces.