Vulnerability Type: DOM-based Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)

Attack Vector
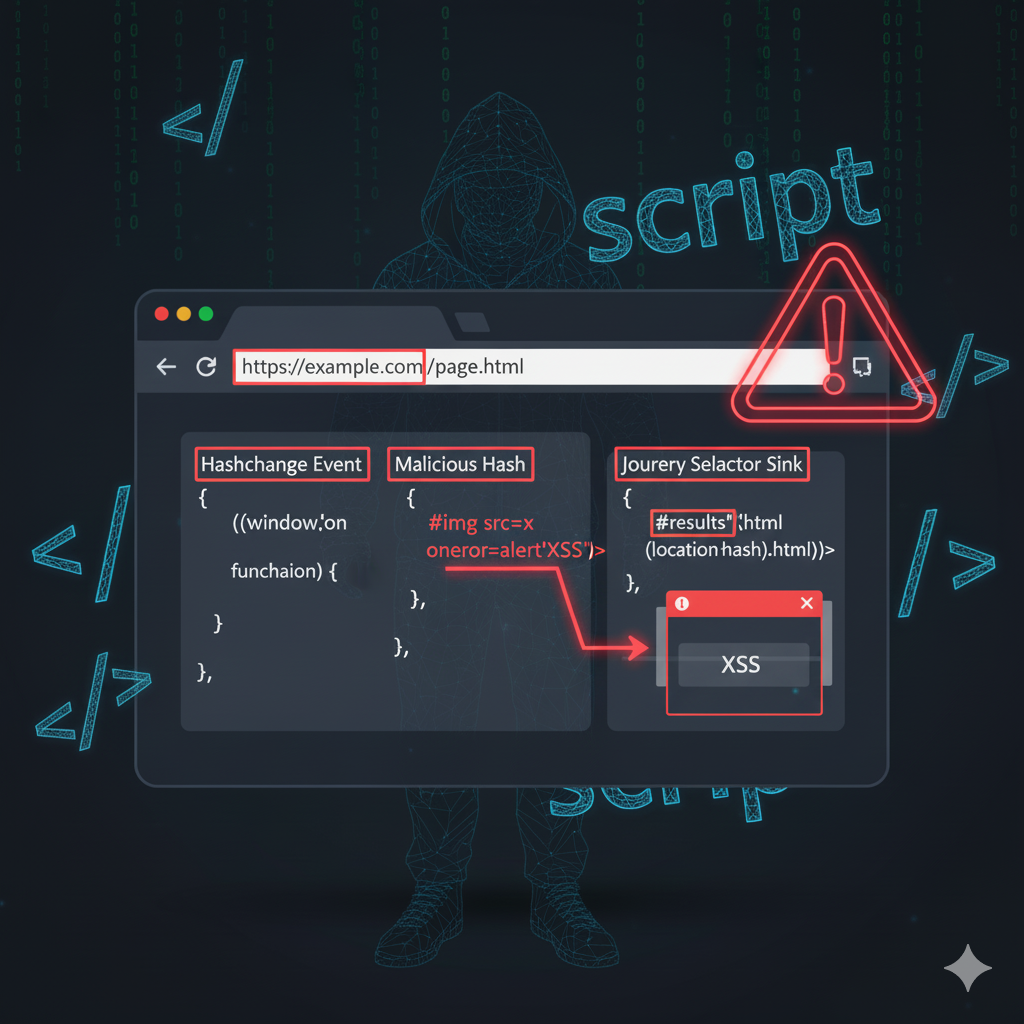
The vulnerable application uses jQuery to dynamically process the URL fragment identifier (`#`) and injects it unsafely into the DOM. By exploiting the `hashchange` event, an attacker can trigger malicious JavaScript execution when the victim interacts with a crafted URL.
Exploitation Steps
- Identify the Vulnerability:
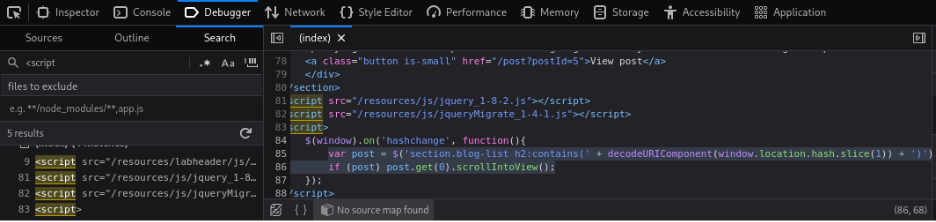
- The application listens for the `hashchange` event and uses jQuery to select and manipulate DOM elements based on the URL fragment (e.g., `#example`).
- The fragment is inserted into the page without proper sanitization, creating an XSS sink.
- Craft the Malicious Payload:
- Create an `<iframe>` that loads the target page with a malicious fragment:
<iframe src=https://YOUR-LAB-ID.web-security-academy.net/# onload="this.src+='<img src=x onerror=print()>'" ></iframe>
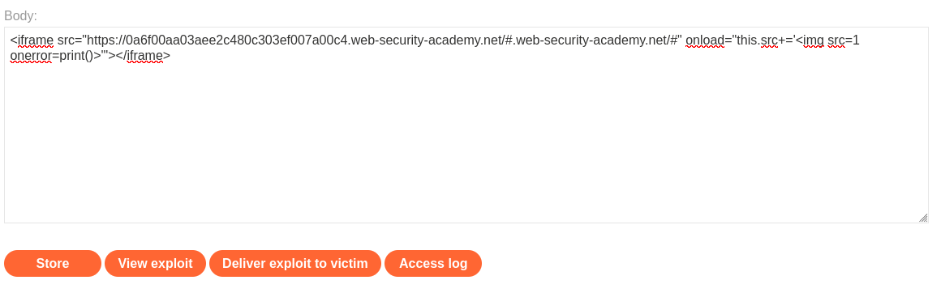
- When the `<iframe>` loads, it appends an `<img>` tag with an `onerror` handler to the fragment, triggering the `print()` function.

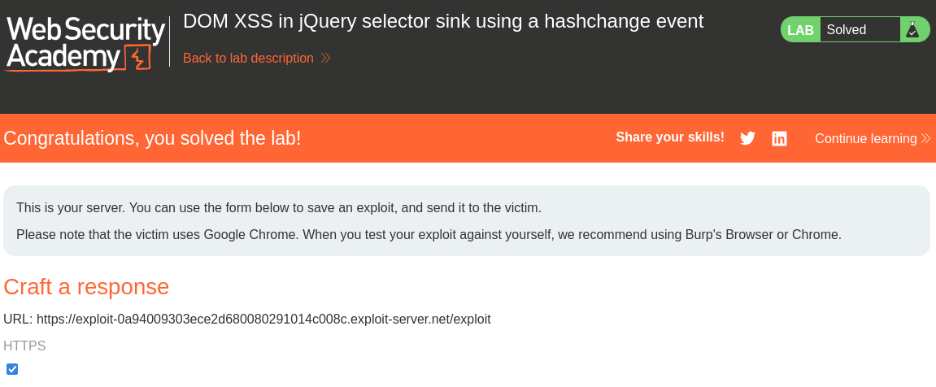
- Deliver the Exploit:
- Host the payload on the Exploit Server and click “Deliver to victim”.
- When the victim visits the malicious page, the `hashchange` event fires, and the unsanitized fragment executes the payload.
- Confirmation:
- The `print()` function is called, confirming successful XSS exploitation.
Mitigation Strategies
- Sanitize URL Fragments: Validate and sanitize any input derived from `location.hash` before processing it with jQuery.
- Avoid Unsafe jQuery Methods: Replace risky methods like `$()` (selector injection) with safer alternatives like `document.getElementById()`.
- Use `data-` Attributes: Store dynamic content in `data-` attributes instead of injecting raw HTML.
- Implement Content Security Policy (CSP): Restrict inline scripts and unsafe `eval()` to mitigate the impact of XSS.
- Disable `hashchange` Manipulation: If the `hashchange` event is unnecessary, remove or secure its handlers.
Key Takeaway
This lab demonstrates how unsafe handling of URL fragments in jQuery can lead to DOM XSS. Attackers exploit the `hashchange` event to inject malicious payloads, bypassing traditional server-side defenses.