Vulnerability Type: DOM-based Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)

Attack Vector
The vulnerable application dynamically sets the `href` attribute of an anchor (`<a>`) tag using untrusted input from `location.search` (URL parameters) without proper sanitization. By injecting a `javascript:`pseudo-protocol payload, an attacker can execute arbitrary JavaScript when the link is clicked.
Exploitation Steps
- Identify the Sink and Source
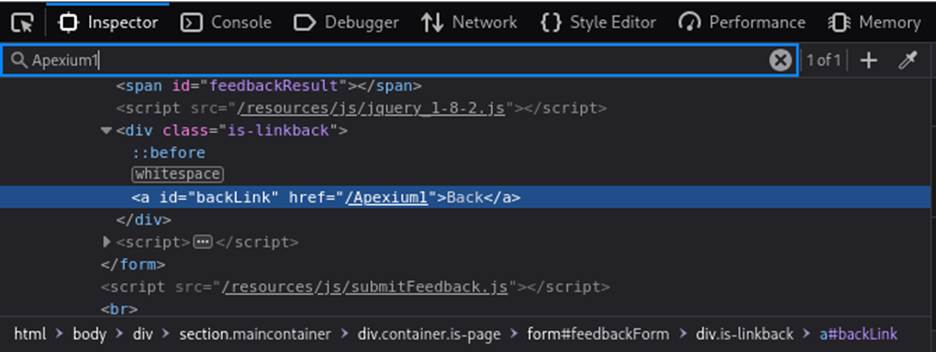
- The `returnPath` URL parameter (e.g., `?returnPath=/test`) is unsafely used to set an `<a>` tag’s `href` attribute via jQuery.
- Inspect the “Back” button/link and observe: <a href=”/test”>Back</a> <!– User-supplied value injected here –>
- Craft Malicious Payload:
- Modify `returnPath` to a `javascript:` pseudo-protocol payload: javascript:alert(document.cookie
- The full URL becomes: https://vulnerable-site.com/feedback?returnPath=javascript:alert(document.cookie)
- Trigger the Exploit:
- Paste the malicious URL or submit it manually.
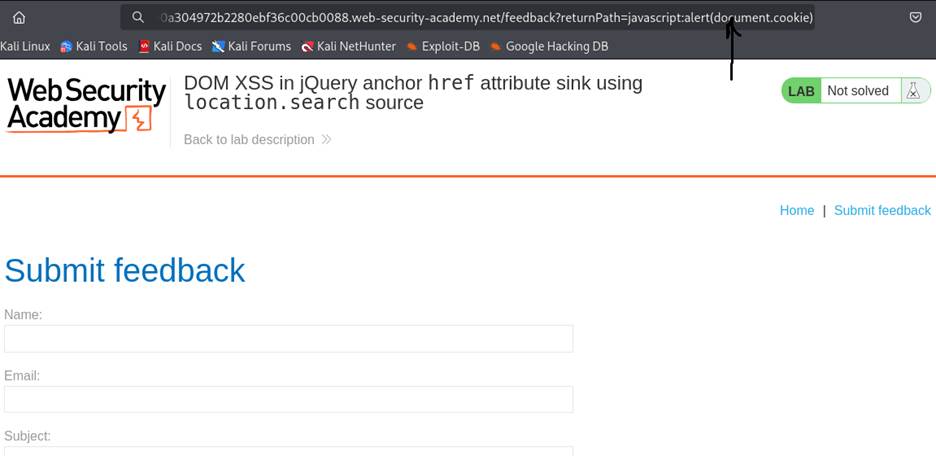
- Click the “Back” button/link.
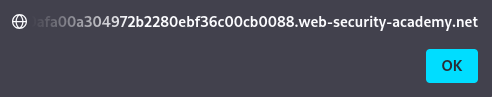
- The `href` attribute executes the JavaScript, leaking the user’s session cookies via `alert(document.cookie)`.
Mitigation Strategies
- Sanitize Dynamic `href` Attributes:
- Strip `javascript:` and other dangerous protocols using allowlists (e.g., `http://`, `https://`).
- Use `encodeURIComponent()` for untrusted URLs.
- Avoid jQuery’s Unsafe Setters: Replace `.attr(“href”, userInput)` with `.attr(“href”, sanitizedPath)` or safer methods like `.text()`.
- Content Security Policy (CSP): Restrict `javascript:` in URLs via CSP with `unsafe-hashes` or `strict-dynamic`.
- Framework Protections: Modern frameworks (React, Angular) auto-sanitize dynamic attributes by default.
Key Takeaway
This lab illustrates how client-side DOM manipulation with untrusted URL parameters can lead to XSS via unsafe `href` attributes. Unlike traditional XSS, this attack leverages the `javascript:` protocol, bypassing server-side mitigations.





