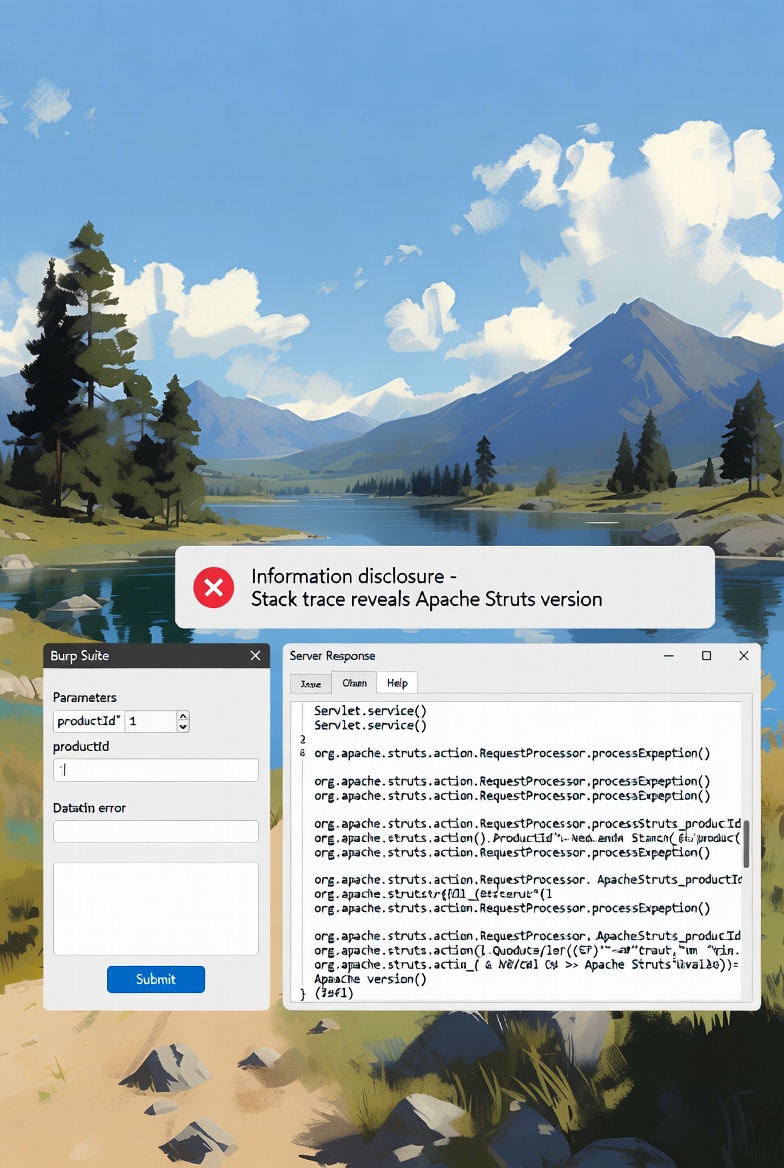
In this lab, the application is vulnerable to information disclosure through detailed error messages. When unexpected input is provided to the server, it responds with a stack trace that reveals internal framework details. This type of vulnerability can expose sensitive technical information that attackers can leverage for further exploitation
Attack Vector Used:
The attack vector involves manipulating the `productId` parameter in the HTTP request to the product page. By providing unexpected input, such as a string instead of an integer, the application throws an exception. The error response includes a detailed stack trace, which inadvertently discloses the underlying technology stack, including the version of Apache Struts being used.
Exploitation Steps:
- Identify the Target Request: With Burp Suite running, navigate to a product page and observe the HTTP history. Locate the GET request that includes the `productId` parameter.
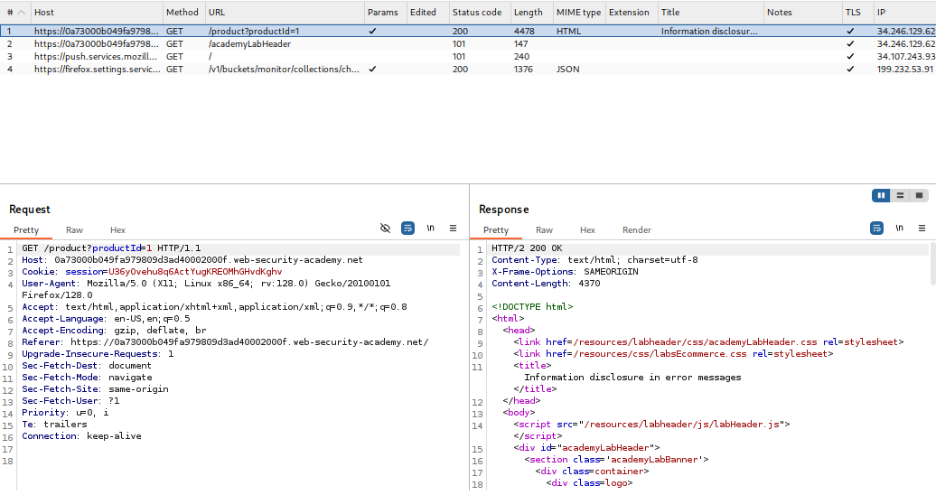
- Send to Repeater: Forward the request to Burp Repeater for manipulation.
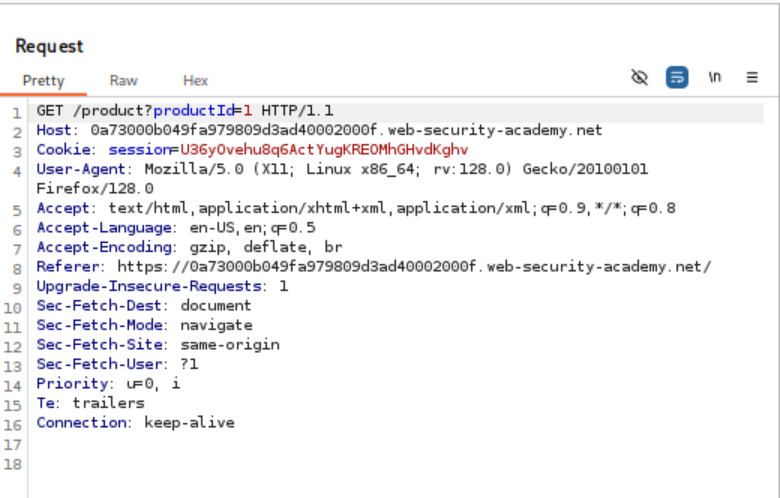
- Modify Parameter: Change the value of the `productId` parameter to a non-integer type, such as a string (e.g., “Apexium”).
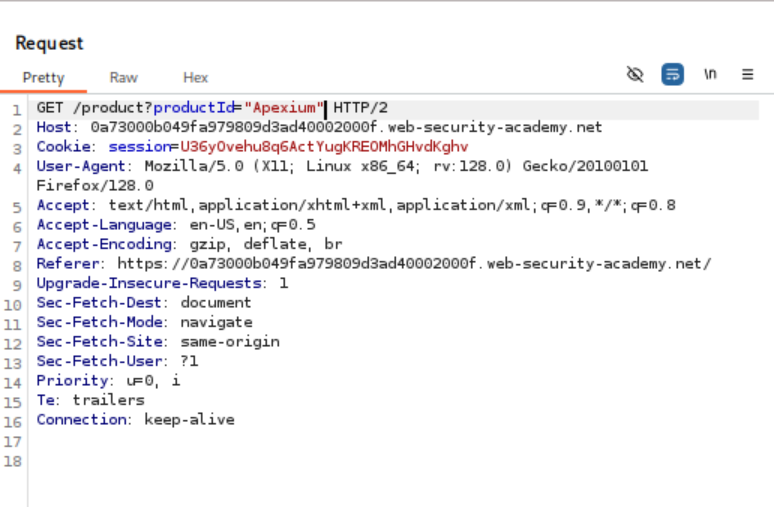
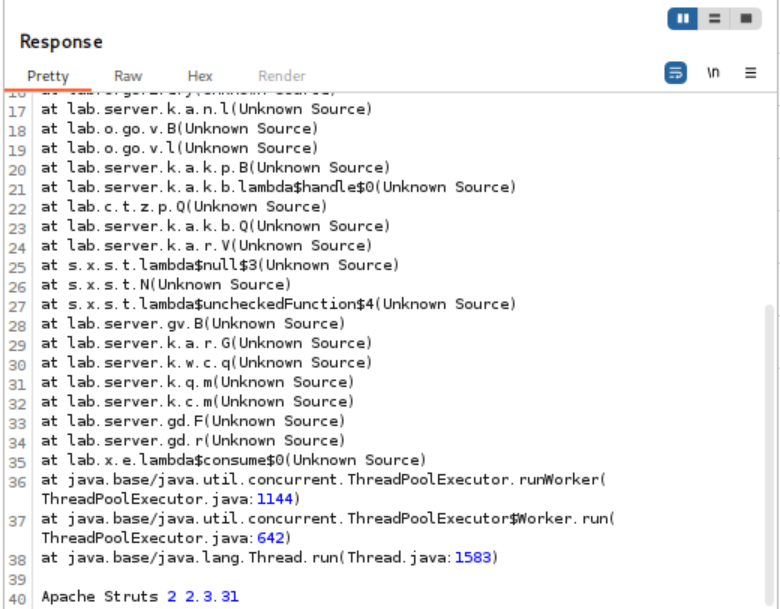
- Trigger Exception: Send the modified request. The server responds with a detailed error message, including a stack trace.
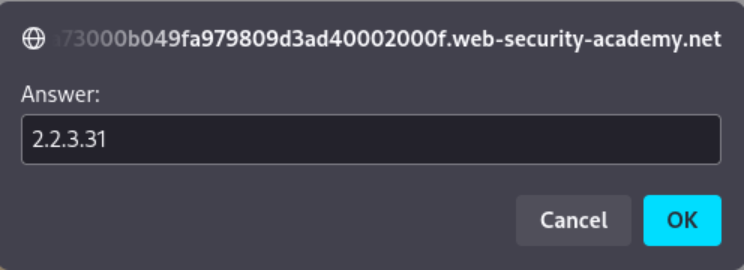
- Extract Information: From the stack trace, identify the version of Apache Struts (e.g., 2.3.31). This information can be used to research known vulnerabilities in that version.
- Solve the Lab: Submit the discovered version number to complete the lab.

Mitigation Strategies:
- Generic Error Messages: Ensure that error messages presented to users are generic and do not expose technical details. Custom error pages should be used to avoid revealing stack traces or framework information.
- Input Validation: Implement strict input validation to handle unexpected data types gracefully. This can prevent exceptions that lead to information disclosure.
- Error Handling Configuration: Configure the application server and frameworks to suppress detailed error messages in production environments. Logging should capture detailed errors for developers while only generic messages are shown to users.
- Security Testing: Regularly test applications for information disclosure vulnerabilities using tools like Burp Suite. Automated scanners can help identify instances where detailed error messages are exposed.
By following these practices, developers can reduce the risk of exposing sensitive information through error messages, thereby strengthening the application’s overall security posture.